Address
304 North Cardinal
St. Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Address
304 North Cardinal
St. Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
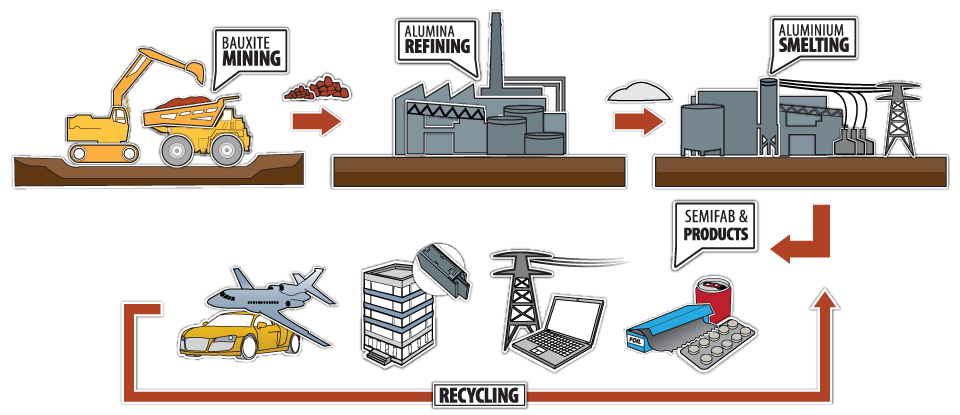
Aluminum might just be one of the most fascinating metals we use today. It’s everywhere – from kitchen foil to airplanes, and it has a pretty intriguing story. But have you ever wondered: how is aluminum made?
Well, you’re about to find out! We’re going on a journey from the raw material, bauxite, all the way to the shiny aluminum products we use every day.
Alumina, or aluminum oxide, is the intermediate step in producing aluminum. Let’s explore how bauxite becomes alumina.
Now we get to the heart of aluminum production – the Hall-Héroult process. This is where the magic happens!
Now that we have pure aluminum, let’s talk about shaping it into something useful. That’s where smelting comes in.
Bauxite is the primary raw material for aluminum production. It’s a reddish-brown ore that contains high concentrations of aluminum hydroxides like gibbsite, boehmite, and diaspore. These minerals are where the magic begins. They’re mixed with iron oxides and other impurities, making bauxite quite the diverse mix. Interestingly, despite its unassuming appearance, bauxite is the primary source of the world’s aluminum.
Did you know that although aluminum is the most abundant metal in the Earth’s crust, it’s never found free in nature? That’s right, it always exists combined with other elements, which is why extracting it is such a fascinating process. This journey from bauxite to aluminum is a story of transformation, one that revolutionized industries and our daily lives.
Let’s talk about bauxite a bit more. This ore is the starting line for aluminum. Bauxite is usually strip-mined because it’s typically found near the surface of the Earth.
The process of mining bauxite isn’t overly complicated, but it’s the refining that’s the real game-changer.
The fact that most bauxite deposits are located near the equator adds a geographical twist to this tale. Countries like Australia, China, Brazil, and India lead the pack in bauxite mining.
Bauxite’s journey to becoming aluminum is a global affair, intertwining geology, geography, and industrial ingenuity.
It’s a process that’s been refined over decades, turning a once-rare metal into an everyday commodity.
And here’s a fun fact: The first commercial extraction of alumina (Al2O3) from bauxite has been attributed to Henri Sainte-Claire Deville in about 1854.
Extracting aluminum from bauxite is a two-step process.
First, we need to refine bauxite to produce alumina (aluminum oxide). This is done through a process called the Bayer Process. In this process, bauxite is mixed with sodium hydroxide, which dissolves the alumina.
The other substances in bauxite remain solid, separating out. The alumina solution is then cooled and precipitated out as crystals, which are then washed and heated to remove water.
This process seems straightforward, but it’s a fine-tuned balance of chemistry and engineering.
The transformation from a muddy ore to a white powder (alumina) is like watching a magic trick unfold.
And here’s something to ponder: Did you know that for every ton of aluminum produced, about two to three tons of bauxite are processed? That’s a lot of raw material for just a bit of metal!
After alumina, we enter the realm of the Hall-Héroult Process. This is where the alumina is transformed into actual aluminum.
Named after its American and French inventors, the process involves dissolving alumina in molten cryolite and then passing a direct electric current through it. This causes the aluminum to separate from the oxygen. What’s left is pure, molten aluminum.
The Hall-Héroult Process is the backbone of aluminum production. It’s an electrifying spectacle (pun intended) of chemistry and electricity working together.
This process is so critical that the invention of the Hall-Héroult Process is often considered the birth of modern aluminum production.
It’s like the secret recipe that turned aluminum from a precious metal more valuable than gold into something we wrap our sandwiches in.
Diving deeper into the Hall-Héroult Process, it’s a marvel of electrochemistry. Inside large carbon-lined steel containers called pots, the alumina is dissolved in a molten bath of cryolite at temperatures around 950 degrees Celsius.
When electricity is passed through this mixture, it breaks down the alumina into aluminum and oxygen. The aluminum sinks to the bottom of the pot, where it’s periodically tapped off.
This process is not only a cornerstone of aluminum production but also a testament to human ingenuity.
It’s amazing to think that this method, developed in the late 19th century, is still the primary way we produce aluminum today. It’s a classic example of a good idea standing the test of time.
And speaking of time, did you know that the aluminum foil in your kitchen likely started its journey thousands of miles away, possibly several years ago?
After the alumina is transformed into aluminum through the Hall-Héroult Process, we move to the smelting stage. This is where the aluminum gets its final form.
The smelting process involves pouring the molten aluminum into molds, where it solidifies into large slabs called ingots.
These ingots can be further processed into a variety of products like sheets, coils, or even foil.
Smelting is the grand finale in the aluminum production process. It’s where the metal gets its strength and versatility.
The incredible part about aluminum smelting is its efficiency. Aluminum’s lightweight nature combined with its ability to be recycled endlessly without losing quality makes it a superstar in the metal world.
Did you know that recycling aluminum saves around 95% of the energy required to make the same amount from raw bauxite?
The aluminum smelting process isn’t just about melting and pouring. It’s a carefully controlled procedure to ensure the highest quality of the metal. The temperature, the purity of the alumina, and the timing all play crucial roles in determining the quality of the final product. The molten aluminum is often treated to remove impurities and to achieve the desired alloy composition.
This stage of production is where aluminum’s properties are fine-tuned to suit its end use. Whether it’s for aircraft parts that require high strength or for packaging materials that need to be lightweight, each application has its unique requirements. It’s fascinating to think that the soda can you’re drinking from was once a combination of bauxite and electricity, transformed through a series of complex processes.
Bauxite mining is a global story, with the ore being mined in many parts of the world. The top producers include Australia, China, Brazil, and India. Each region has its own story and method of mining, adding to the rich tapestry of aluminum production.
The global nature of bauxite mining highlights not just the importance of aluminum, but also how interconnected our modern industrial processes are.
The journey of aluminum is a testament to global trade and cooperation. It’s incredible to think that the aluminum in your car or your kitchen may have started its journey on the other side of the world.
When we zoom in on the primary sources of bauxite mining, we see a diverse range of landscapes and techniques.
Australia, the world’s largest producer, boasts large, open-pit mines. China, on the other hand, combines its bauxite mining with other minerals extraction, making it a multi-faceted operation.
Brazil and India also play significant roles, each with their unique mining landscapes and methods.
This global network of bauxite mining is a fascinating look at how natural resources are tapped and transformed.
Each country’s approach to mining reflects its geography, technology, and economic strategies.
And here’s an interesting nugget: The town of Bauxite, Arkansas, in the United States, was once a major source of the ore and is where the mineral got its name.
One aspect of aluminum production that can’t be overlooked is its energy consumption. Producing aluminum is a power-intensive process, especially during the smelting stage.
The amount of electricity used in this stage is staggering. It’s estimated that about 5% of the total global electricity consumption is used in aluminum production.
Despite being energy-intensive, there’s a silver lining. The aluminum industry has been working tirelessly to improve its energy efficiency.
Technologies like improved electrolytic cells in the smelting process have significantly reduced energy consumption. Moreover, the recyclability of aluminum plays a huge role in reducing the overall energy footprint of the metal.
But why is aluminum production so energy-intensive? It boils down to the need for constant, high temperatures and the electrolysis process in the Hall-Héroult method.
This process requires a lot of electrical energy to break down alumina into aluminum and oxygen. It’s a trade-off of sorts – the energy input is high, but the output is a metal that’s incredibly useful and recyclable.
From bauxite mining to the Hall-Héroult process, and finally to smelting and recycling, the journey of aluminum is truly remarkable. It’s a story of innovation, perseverance, and science working together to produce a metal that has become indispensable in our daily lives.
Understanding how aluminum is made involves exploring the processes of extraction and refinement from bauxite ore. To gain a deeper appreciation of aluminum production and how it compares to the manufacturing and extraction processes of other metals, explore the following resources:
If you also want to learn more about some other less common metals, their uses, history, facts and much more here we have some other honorable mentions worth checking out:
By exploring these different metals and their production processes, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of how aluminum is made and how its production compares with the unique characteristics and manufacturing techniques of other essential materials.
As we strive for a more sustainable future, aluminum’s role only becomes more crucial. Its recyclability and versatility make it a key player in green technologies and a model for sustainable practices in the metal industry.