Address
304 North Cardinal
St. Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Address
304 North Cardinal
St. Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM

Today we’re exploring the top uses for Palladium; The lustrous, silver-white metal, may not be a household name like gold or silver, but its significance in today’s world is hard to overstate.
With a variety of applications that span numerous industries, palladium has firmly established itself as a metal of the future. Stick around as we delve into the numerous facets of this intriguing element.
There’s a reason investors are buzzing about palladium. This remarkable metal boasts a range of uses, from tech and industry to medicine and jewelry.
Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or simply curious, you’re likely interacting with palladium in ways you didn’t even realize.
If you’d like to watch a short summary of Palladium’s various uses in a short video, we’ve included one at the bottom of this post.
So, let’s dive in and uncover the world of palladium!

If you’re a tech aficionado and you have the time and pacience, did you know that you can recover palladium from hards discs and other tech items?
Our tech-driven world leans on metals like palladium to keep innovating and evolving. Ever wonder why?
Here’s a fun fact: your electronic devices, especially those integrated circuits, probably rely on palladium.
This metal offers excellent conductivity and resistance to oxidation, making it indispensable in semiconductor tech.
From smartphones to high-end computing devices, palladium’s touch is everywhere, ensuring that our devices work seamlessly.
These are some gadgets made using palladium:
As the world pushes towards a greener future, palladium emerges as a clean energy champion.
Central to fuel cells, palladium helps generate electricity through chemical reactions, minus the harmful emissions.
Think of vehicles running on hydrogen fuel cells – that’s where this metal plays a pivotal role.
Its efficiency and reliability make it a top pick for green tech innovators.
Items made using palladium:
The automotive sector and palladium share a special bond. Wondering how? Let’s explore.

If you’re environmentally conscious (and who isn’t these days?), you’d be thrilled to know that palladium is a star player in reducing harmful car emissions. Found in catalytic converters, palladium triggers chemical reactions that turn toxic gases into less harmful ones.
It’s a vital reason why the air we breathe is cleaner than it was decades ago.
For the car enthusiasts and green energy advocates, here’s where things get exciting.
Palladium’s unique ability to absorb hydrogen makes it crucial in hydrogen purification, a step essential for fuel cell vehicles.
As we shift gears towards sustainable transportation, palladium is sure to be in the driver’s seat.
Beyond tech and cars, palladium has some serious industrial prowess.
By now, you’ve probably caught on that palladium is an environmental ally. Its use in industries not only propels efficient processes but also ensures reduced emissions and waste.
This is mainly achieved by moving from platinum or rhodium based catalytic converter to Palladium catalytic converters.
They are cleaner and help reduce carbon emissions because of palladiums unique properties.
From cleaner air to purer water, the environmental footprint of palladium is undeniably positive.
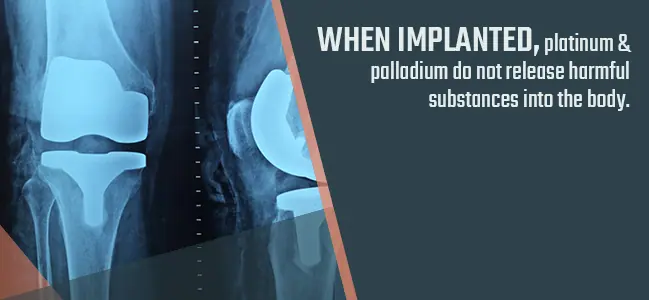
Our health and well-being owe a bit to palladium. Intrigued? Let’s unravel this connection.
That shiny dental crown or bridge? There’s a good chance palladium is in there. Renowned for its biocompatibility and strength, palladium is often mixed with gold or silver in dental alloys. Its resistance to corrosion ensures that our dental fixtures last long and stay safe.
Dentistry Items made using palladium:
Stepping into the world of medical treatments, palladium has made noteworthy contributions.
Used in specific cancer treatments, like prostate cancer, palladium-103 can be used as a radiation source.
Its ability to target and treat cancer cells showcases the metal’s invaluable role in medicine.
Radiopharmaceutical Items made using palladium:
Beyond its industrial might, palladium has a softer, aesthetic side. Jewelers around the world cherish it for its lustrous finish and durability.
Whether it’s a shiny ring or a delicate necklace, palladium ensures that our ornaments don’t just look good, but also stand the test of time.
Plus, for those with sensitive skin, palladium’s hypoallergenic properties are a blessing.
Jewelry Items made using palladium:
Life’s everyday moments are sprinkled with a touch of palladium. From the watch ticking on your wrist to certain types of photography, the magic of palladium is omnipresent. Its durability, resistance to corrosion, and versatility make it a favorite choice in many daily use products.
Everyday Items made using palladium:
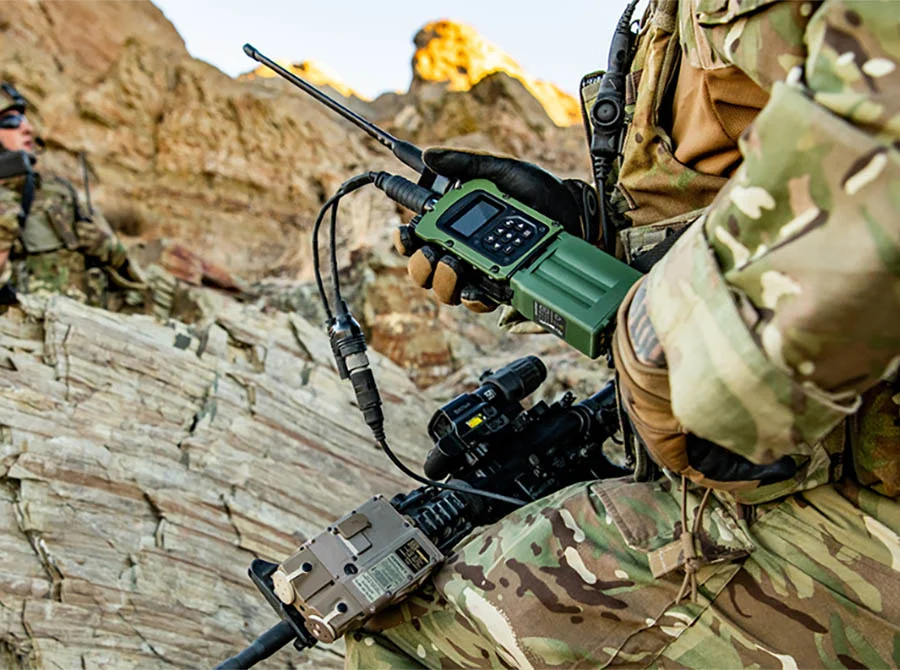

Defense and security have always been critical, and palladium plays a unique role in these sectors.
Modern warfare and defense strategies are highly reliant on cutting-edge electronics and communication systems. Palladium, with its incredible conductivity and resistance to corrosion, is a vital component in many of these military-grade devices.
These are some of the comms Items made using palladium:
The military often employs sensitive detection and sensing equipment, which require materials that can provide reliable performance.
Palladium, being highly reactive with certain chemicals, makes it ideal for specific detection applications.
Detection and sensing equipmentItems made using palladium:
The drive to harness energy in efficient and safe ways has always been at the forefront of technological advancements. And when we talk about nuclear reactors, the need for reliable and durable materials is paramount. That’s where palladium comes into the picture.
In the world of nuclear energy, controlling the rate of reactions is critical. Palladium, with its high neutron capture cross-section, can be employed in fast breeder reactors.
These reactors aim to produce more fissile material than they consume, and palladium acts as a safety component, absorbing excess neutrons and maintaining the reactor’s stability.
Nuclear reactors often produce tritium, a hydrogen isotope, as a byproduct. Palladium’s unique property to selectively absorb hydrogen and its isotopes makes it instrumental in the process of separating and purifying these isotopes.
This not only aids in the safety protocols of reactors but also has potential applications in future fusion reactors.
System made using palladium:
Research is ongoing into the development of palladium-alloy membranes that can potentially improve the efficiency of nuclear reactors.
These membranes, thanks to palladium’s unique properties, could provide better heat and radiation resistance, thereby enhancing reactor safety and longevity.
Items made using palladium:
The world of palladium is vast, fascinating, and brimming with possibilities. From safeguarding our environment to enriching our lives with tech and aesthetics, this metal truly shines in versatility.
As we continue to innovate and seek sustainable solutions, it’s evident that palladium will be right there with us, guiding the way forward.
And there you have it! An immersive journey into the multifaceted world of palladium. Whether you’re considering investing, fascinated by tech, or simply curious, this metal has something for everyone.
If you’re curious about other common metals like copper and iron or even rare metals like ruthenium, tantalum or rhodium and their uses be sure to check out our other posts!
Thank you, dear reader for sticking with us to the end, we sincerely hope this information was of help to you, have a fantastic day!